Separation Anxiety Disorder
Separation anxiety involves feelings of fear associated with separation from specific persons or an individual, or at times, a pet. This term is most commonly associated with children, however, adults can also experience this. It can be a sign of a condition called separation anxiety disorder which can be more serious.
If this separation anxiety is persistent and seems to interfere with your child’s, or your own overall wellbeing, then it’s an indication towards the development of separation anxiety disorder.
Separation anxiety disorder can result in panic attacks and physical symptoms like nausea, headache, sore throat, ulcers, etc. In children, this condition begins at an early age starting from preschool and may continue on in adulthood if left untreated.
Separation Anxiety Symptoms
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Health Conditions (DSM-5) specifies certain symptoms of separation anxiety, and if you feel any or all of these symptoms, you must visit a doctor or a mental health professional.
Separation anxiety involves symptoms that are experienced in other anxiety disorders, as well as symptoms associated with this specific condition. The signs and symptoms of separation anxiety are as follows:
- Abnormal or intense stress and anxiety attached with separation from a pet or a person or a group of people
- Feelings of worry, listlessness and hopelessness over being alone
- Fear that someone may be harmed if they leave them
- Fear of being left alone and feeling lonely
- Physical symptoms felt when they know that they are going to be separated from their spouse or someone they are attached to, or on separation from this person
- The need to know where their loved ones or friends are no matter what time it is
- Recurrent nightmares involving separation from a loved one
- Stomachaches, headaches, etc. felt on separation from the person that they are attached to
The symptoms of separation anxiety can last upto 6 months in adults. They may also experience panic attacks in chronic cases, which involves feelings of intense anxiety rising to a peak when thoughts of triggering stimuli are present.
Additionally, children may refuse to go to bed without their parent or caregiver, or the person that they are attached to. They may experience nightmares in which they experience separation from this individual. They feel excessive distress when they leave for school, and find it difficult to be away from their caregiver or parent.
Separation Anxiety in Adults
Separation anxiety tends to have its roots in early childhood and may be due to factors like early separation from a caregiver or a parent. It can also stem from being separated from a partner. It can also be a sign of other underlying mental health problems like psychotic disorders or autism spectrum disorder.
Adults with separation anxiety disorder have a tough time dealing with any or every situation in which they are away from their loved ones. This can include being away at work, or being at home while the children are at school and the spouse is at work, or going out for shopping or daily tasks without a family member, etc. Even thinking about being away or planning trips to the market or out-of-station trips for business-related purposes, people with separation anxiety struggle with overwhelming feelings of listlessness, constant worry and stress.
Separation anxiety is a debilitating condition. By the time we grow out of adolescence and step into adulthood, we develop emotional skills that help us understand and deal with brief periods of being away from family and spouses easily. However, adults with separation anxiety feel extreme distress and anxiety on separation, to the extent that it is developmentally inappropriate.
Adults with separation anxiety may be described as being overly protective or controlling of their family members and children, however, this can be seen as their way of expressing their fears associated with separation.
Separation Anxiety in Children and Infants
Among children, it may be considered normal to have feelings of anxiety and display clinginess every time they have to leave for preschool or go for a hobby class. Throwing tantrums, crying, or hiding behind the parent’s back and not leaving their side might be, in most cases, nothing more than healthy reactions to being separated from a parent. This is normal for certain stages of development and you may have no reason to worry about your child. However, some children may struggle with separation anxiety that may be intense and come with more troubling symptoms than regular separation anxiety that is developmentally appropriate.
Up till the age of four, children are expected to feel these sentiments and display signs of separation anxiety. However, if they are experiencing more intense and chronic symptoms that are troubling them day and night and interfere with their normal activities, it is time to consider seeing a child’s specialist or a child psychologist. Such children experience the symptoms of separation anxiety which might be more chronic or intense than others, and stay with them even during elementary or middle school.
Ideally, such fears must fade away once the child gets older. If such problems persist, then it may be an indication that your child has developed separation anxiety disorder. Early diagnosis and treatment help reduce the symptoms and provide significant relief.
Separation Anxiety Treatment
The treatment for separation anxiety involves psychotherapy, and anti-anxiety medication.
Psychotherapy often involves the use of cognitive behavioral approach, which aims to help the person identify their behaviours and thought patterns which are deteriorating their condition or might be the reason they have the condition. Moreover, both adults and children benefit from group and family therapy.
In addition to this, parents are also encouraged to learn parenting skills which enable their children to learn social and emotional skills and achieve developmental milestones in a consistent manner. Clients are also encouraged to join support groups as they help in learning skills which counter separation anxiety.
Anti-anxiety medication is temporarily prescribed in cases where people feel chronic and intense symptoms. However, drugs are not to be taken in the long term and do not help in eliminating the condition or the symptoms. Some types of anti anxiety drugs are also known to be addictive.
How To Deal With Normal Separation Anxiety in Children?
For children who experience normal separation anxiety, there are some steps that their parents can take to help them cope and deal effectively with their emotions.
Practice saying goodbye and brief periods of separation. You could start with 15 minutes of leaving the child alone in a room, and then for an hour at a caregiver’s place. In this way, gradually, the child would become accustomed to handling separation for a while.
Moreover, the caregiver should be consistent, you must not switch between one person to another as it may be discomforting for your child. Try to let the child be in familiar surroundings whenever you leave, or try to make new surroundings familiar by giving them a stuffed toy or any other familiar object that they may be attached to.
Also, when you’re going away from the child, do not make the goodbye ritual too long or dramatic. Simply say that you will be coming back after a while.
Moreover, try to minimize media including television that may arouse fear or worry. A strict no to anything that is frightening.
Lastly, do provide your child with enough care, affection and attention and do not forget to do so while you’re trying to condition them to be comfortable with separation. Your child will be fine. However, if you suspect that there are indications or symptoms of social anxiety disorder, you must consider proper treatment as it is a serious condition that negatively affects your child’s mental and physical well being.
Frequently Asked Questions about Separation Anxiety
Q. How long does “normal” separation anxiety last?
Separation anxiety tends to peak between ten to eighteen months and then gradually, it fades away as the child grows up to be about two and a half years old. This phase of the emotional development is critical and sensitive both for the child and for you. For others, it might even be difficult and painful to deal with.
Q. How does separation anxiety affect sleep?
When the child is one and a half years old, separation anxiety can cause disruptions in the sleep pattern and many sleepless nights for the child. This phase lasts for several months. In this, the child may wake up several times during the night and cry as well as show signs of anxiety for a parent or both the parents (often they express a strong preference for one parent).
Submit a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Recent Blogs
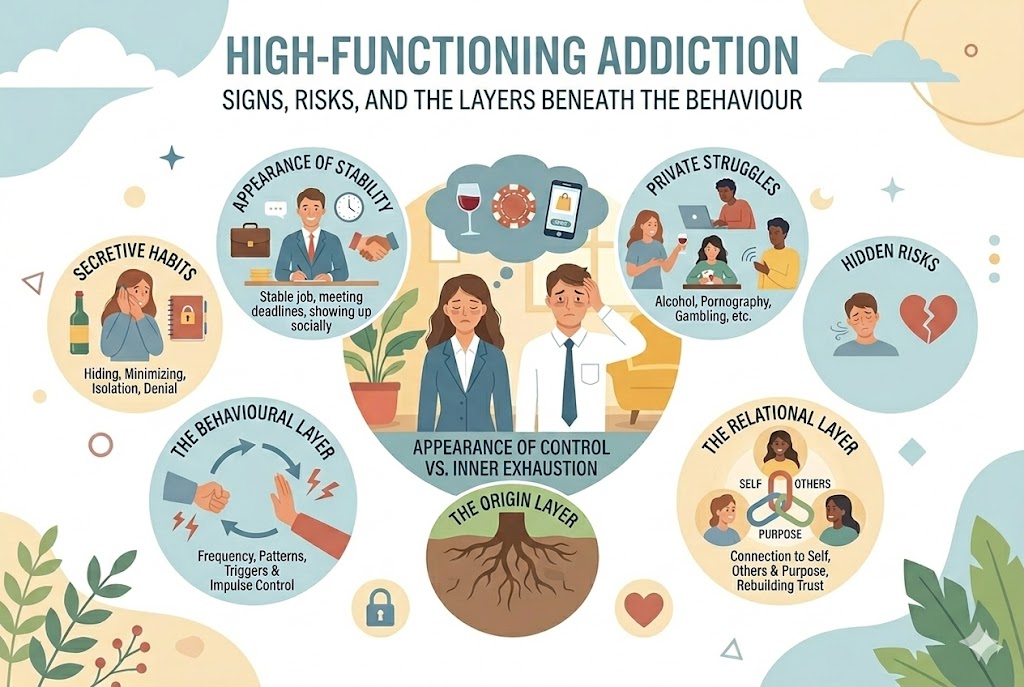
High-Functioning Addiction: Signs, Risks, and the Layers Beneath the Behaviour
5 March, 2026
Addiction isn’t always visible. Some individuals continue to work, parent, meet deadlines, and show up socially – all while privately struggling wi...
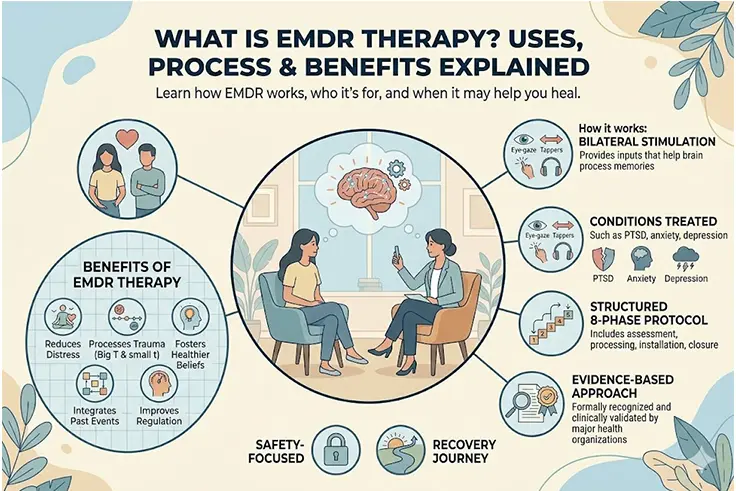
What Is EMDR Therapy? Uses, Treatment & Benefits Explained
2 March, 2026
What is EMDR therapy? EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitisation and Reprocessing) therapy is an evidence-based approach that helps individuals process and heal fr...
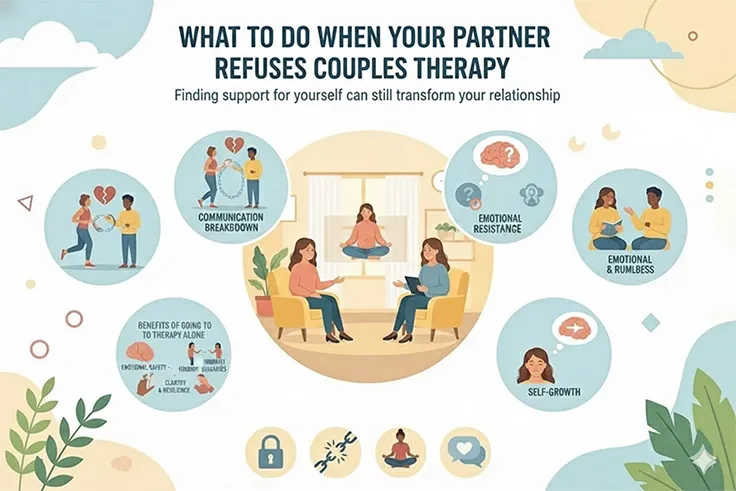
What to Do When Your Partner Refuses Couples Therapy
6 February, 2026
When a partner refuses couples therapy or a partner doesn’t believe in therapy, it can leave you feeling stuck, alone, and carrying the emotional weight ...